TCFD
Communication on Recommendations of Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
DISCO CORPORATION fully endorses the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)*.
Based on the TCFD’s framework, the DISCO group will appropriately assess and manage climate-related risks and opportunities, and proactively communicate with the general public.
*Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD):
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) created the TCFD in 2015 at the G20’s request in order to consider and discuss corporations’ disclosure of information regarding climate change in order to support financial institutions. It recommends that corporations disclose their governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets regarding climate change-related risks and opportunities.
TCFD Official Website:https://www.fsb-tcfd.org/
Governance
The DISCO group recognizes that climate change is an important management issue, and has implemented a Company-wide Environmental Committee, in which the Managing Executive Officer (Chief Environmental Officer) acts as the chairperson, and the Representative Executive Officer / President and Representative Executive Officer / Executive Vice President are committee members. In addition, Outside Directors also participate in the Company-wide Environmental Committee as observers.
This Company-wide Environmental Committee is held twice a year, and the risks and opportunities affecting business activities in the mid-to-long term are identified and assessed, and countermeasures are considered. Important themes such as our environmental vision, risks and opportunities, and progress towards our goal are discussed and reported to the Executive Committee and Board of Directors at least once a year. In addition, environmental departments have been established at the head office and at all manufacturing sites to promote the relevant measures.
Promotion System

Strategy
Selecting and Analyzing Scenarios
Analysis was conducted mainly by referring to the World Energy Outlook of the International Energy Agency (IEA) and reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
1.5 ℃ scenario (NZE)
This is a scenario where the global energy sector achieves net zero emissions through implementation of the measures and regulations that are needed to realize a decarbonized society, which will lead to a reduction in fossil fuel consumption, which, along with the development of energy-saving technologies, will reduce the overall final energy consumption.
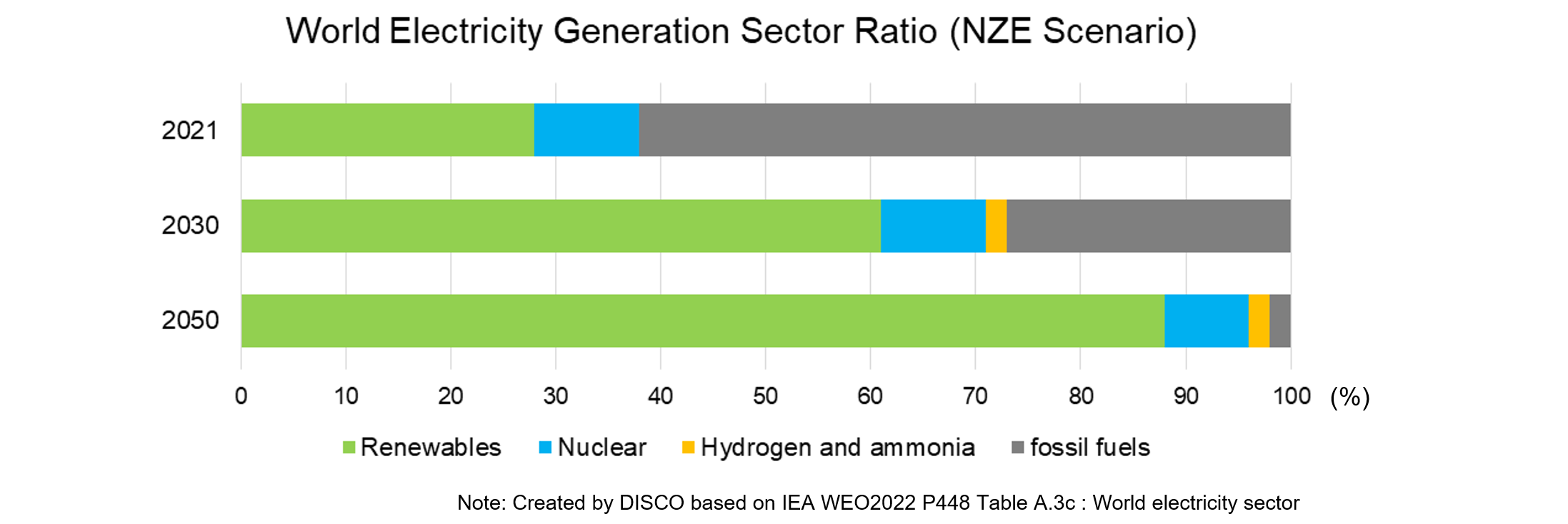
In this situation, renewable electricity generation is predicted to account for approx. 60% in 2030, and 90% in 2050.
Under such circumstances, in both 2030 and 2050, the risks that accompany the transition to a decarbonized society will increase due to the enhancement of countermeasures against climate change implemented by governments around the world, but we have assessed that there will be no significant financial impact on the DISCO group.
On the other hand, the key to realize a decarbonized society lies in semiconductors, and the demand for power semiconductors, that contribute to energy/power saving, is expected to grow. Our assessment indicated that business opportunities will expand over a long period of time for the DISCO group, as we provide comprehensive solutions for semiconductors, including manufacturing equipment, related products, consumables, etc.
As a result, our assessment concluded that moving toward 2050, the business opportunities that come with the increased demand for power semiconductors will outweigh the risks to transition to a decarbonized society.
4℃ scenario
It is plausible that the not much progress will have been made regarding the implementation of regulations, and physical risks will increase due to natural disasters caused by climate change, such as the intensification of heavy rains, flooding, water shortage, and a rise in sea levels.
DISCO implemented the Business Continuity Management (BCM) system in 2003, and has established a department dedicated to BCM activities. We are constantly implementing measures and strengthening our facilities in order to improve our business continuity capabilities by eliminating various external influences including natural disasters.
Risks and Opportunities
The DISCO group has assessed the risks and opportunities regarding how climate change will impact our business activities in the future based on multiple scenarios. The degree of impact on business activities has been assessed in three stages: “major,” “medium,” and “minor.”
In addition, the period in which the risks and opportunities occur has been categorized into two: medium term and long term.
Degree of impact
| Impact | Definition |
|---|---|
| Major | An impact large enough to significantly shrink/expand business activities |
| Medium | An impact on some business activities |
| Minor | No or minimal impact on business activities |
Period in which risks and opportunities occur
| Period | Time span |
|---|---|
| Medium term | Through 2030 |
| Long term | Through 2050 |
Main Risks and Opportunities Regarding Climate Change
| Factors | Expected Major Effects | Impact | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium Term | Long Term | ||||
| Risks | Transitional | Carbon price | Manufacturing and R&D costs increase due to carbon tax and/or emissions trading | Minor | Minor |
| Energy saving, regulations | Handling costs including for green electricity purchases increase due to the demand to switch to renewable energy | Minor | Minor | ||
| Price increase for parts and materials | Procurement costs increase from an increase in demand for materials (rare-earth elements, aluminum, etc.) due to electrification and a shift to EV | Minor | Minor | ||
| Physical | Extreme weather conditions | Costs increase for BCM support and restoring production facilities | Minor | Minor | |
| Sales decline due to a decline in factory operation rates | Minor | Minor | |||
| Sales decline due to procurement delays | Minor | Minor | |||
| Opportunities | Social needs | An increase in the importance of semiconductors due to decarbonization using digital technology | Major | Major | |
| Increased demand for power semiconductors due to energy efficiency and a shift to EV | Major | Major | |||
| Customer needs | An increase in competitiveness due to an improvement in the energy-saving capabilities of products | Major | Major | ||
| An increase in the competitiveness of products by providing solutions corresponding to decarbonization needs | Major | Major | |||
Handling Risks
-
Promotion of Company-Wide Energy-Saving Activities
As a part of activities implemented with the goal of carbon neutrality, the DISCO group promotes energy-saving activities in each division and individual. These activities are company-wide; reduction targets are set for each division depending on their energy consumption (greenhouse gas emissions), and points are given depending on the achievement level. These points are reflected in the employees’ bonuses, promoting behavior modification in each individual and creating a system that achieves self-autonomy. -
Proactive Implementation of Power Generation
In order to reduce the environmental load from business activities, the DISCO group has installed solar power generation systems at each factory and affiliate office worldwide. Recently, in addition to the existing 140 kW solar power generation system, a system with a maximum power generation capacity of 1,054 kW was installed at Chino Plant, Nagano Works, allowing for megawatt-class power generation (1,194 kW in total). In addition, the capacity of Kuwabata Plant at Hiroshima Works was also increased (292 kW). With this, the power generation capacity of the DISCO group as a whole has reached a maximum of 3,649 kW (as of the end of March 2024). -
Promoting Carbon Neutral Literacy
The DISCO group provides training to employees every year with the aim of promoting awareness and understanding regarding energy-saving practices. This training includes social trends, the risks if we do not work on decarbonization and the opportunities if we do, and how to calculate the reduction effects of energy-saving activities. The training is implemented company-wide for the entire global DISCO group using our internal e-learning system. -
Improvement Activities to Achieve Carbon Neutrality
The DISCO group views activities focused on achieving carbon neutrality as an opportunity to become stronger. As part of improvement activities that have monthly reports, a theme for improving energy-saving/carbon neutral practices is also included. These improvement reports are carried out in a 1-minute presentation battle format. The points acquired from winning the battle affect employees’ bonuses, making it a system that promotes proactive involvement from employees. -
BCM Countermeasures
The Business Continuity Management (BCM) system was established in 2003, and in 2012 we became the first Japanese company to acquire ISO 22301. In addition to establishing and operating a BCM Committee comprised of executives including the Representative Executive Officer / President as the chairperson, a designated department for BCM was also established. The BCM Committee is held every month after the Board of Directors meeting, and Outside Directors participate in the committee as observers. In addition, the DISCO group is constantly implementing measures and strengthening our facilities in order to improve our business continuity capabilities by eliminating various external influences including natural disasters. To enhance countermeasures against water risks including heavy rains, water shortages, storm surges, etc., measures such as building breakwaters and improving our water-saving and water recycling ratio are being implemented.
The heavy rain in Western Japan in July 2018 caused severe damage in Kure, Hiroshima, where DISCO’s manufacturing site is located. At the Kure Plant, where blades and wheels are manufactured, there was a water outage for both daily and industrial water, and logistics operations were severely impacted due to the fragmentation of the surrounding roads. Despite this, DISCO was able to fulfill its supply responsibilities without any issues because of its daily BCM activities.
The DISCO Group’s Business Opportunities
Each country has its own policy regarding carbon neutrality for 2050, and preferential schemes such as tax reduction for investments in production facilities of devices and products that contribute to decarbonization, such as power semiconductors, are being considered and implemented.
The DISCO group thinks that it is possible to secure multiple business opportunities, which are steadily increasing as we move toward 2050, by providing optimal solutions for a wide range of materials, processes, and devices, including power semiconductors, using our advanced KKM (Kiru, Kezuru, Migaku) technologies, and by covering all fields that are related to KKM.
Power semiconductors, that play the role of supplying and controlling power, are installed in a wide range of electrical equipment, ranging from familiar household appliances and electric vehicles (EV) to societal infrastructure, including railroads and power transmission / distribution facilities.
In particular, for power generation using renewable energy such as solar and wind, the demand for which will grow as we move toward the realization of a decarbonized society, reducing power loss using power semiconductors will be crucial.
For these reasons, a further increase in demand in the future is predicted for power semiconductors, as they are key devices that will help realize a decarbonized society.
Currently, most power semiconductors are made from silicon (Si) wafers, but next-generation power semiconductors made from silicon carbide (SiC) wafers, that have superior material properties compared to Si, are being developed and used for electric vehicles (EV).
The DISCO group has developed and sells the KABRA process*, which significantly improves the productivity of the SiC wafer manufacturing process, meeting the demand for energy saving, which will further increase in the future.
*KABRA Process: : An ingot slicing method where a separation layer (KABRA layer) is formed at a specified depth by continuously irradiating an ingot with a laser, allowing the ingot to be peeled off from the KABRA layer to form wafers.

Fully Automatic KABRA System
Toward Carbon Neutrality (Transition Plan)
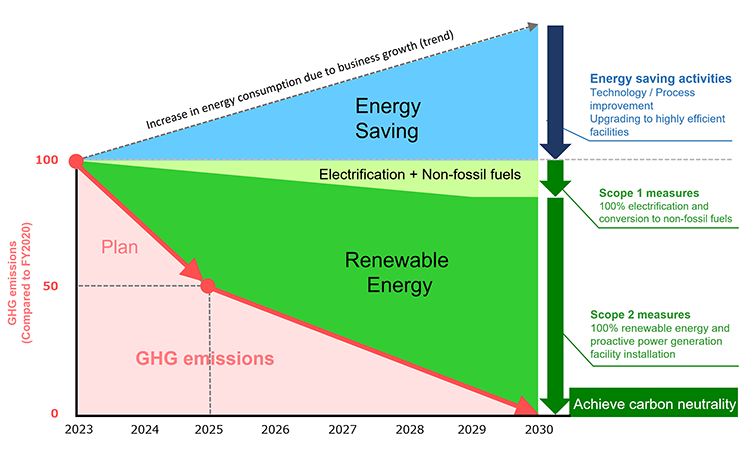
Scope1+2
The DISCO group is aiming to achieve carbon neutrality for Scopes 1 and 2 in 2023.
For Scope 1, the DISCO group will move away from energy that originates from fossil fuels by electrifying and switching to alternative fuels such as e-fuels for all equipment and facilities that use fossil fuels in our business activities.
For Scope 2, the DISCO group’s aim is to not increase our energy consumption even if our business expands, and implement a wide range of energy-saving measures.
Furthermore, the DISCO group plans to achieve carbon neutrality not just by proactively installing power generation facilities such as solar power generation, but also by converting all the purchased power into renewable energy.
Along with the increase of business opportunities that comes with the transition to a decarbonized society, further company growth is expected in the future, due to which an increase in energy consumption is predicted as well. Taking into account that there is a possibility that the price of renewable energy may increase, we believe that our energy consumption needs to be suppressed to a minimum amount.
Therefore, the DISCO group is making an effort to reduce our energy consumption with regard to our sales by having all our employees participate in energy-saving activities, improving our technologies and processes, and upgrading to highly efficient facilities.
Scope3
The DISCO group aims to achieve carbon neutrality for Scope 3 in 2050. Eliminating the emissions that fall under Scope 3 is difficult with just solely the DISCO group’s effort, so we plan to implement measures in cooperation with our customers and suppliers to achieve net zero emissions.
-
Procurement of Raw Materials and Parts
Regarding the raw materials and parts that are used in the DISCO group’s precision processing equipment, precision processing tools (consumables), and functional consumables (chemical products, etc.), the DISCO group is aware that the greenhouse gases that are generated during the manufacturing process of these products is an important issue (Category 1, Scope 3). As an initiative to solve this issue, the DISCO group will promote awareness regarding the emission amount of procured products, and cooperate with our suppliers to procure raw materials and parts with less emissions. -
Transportation and Distribution Related to Procurement
Regarding the emissions that occur during the transportation and distribution of procured materials (Category 4, Scope 3), as procurement is mainly conducted within Japan, the DISCO group will proactively select excellent transportation and distribution methods that are newly being developed in accordance with the evolution of legislations and technological innovation, including a modal shift to next-generation low-emission transportation that uses EVs and e-fuels. -
Emissions Arising From the Use of DISCO Products
The DISCO group is aware that the emissions that are generated from the use of our sold products (Category 11, Scope 3) is also a significant issue.
In 2004, the DISCO group formulated the Green Product Guidelines, which include our policies at the time of design and development so that the environmental impact of a product over its lifetime is minimal. The DISCO group aims to reduce the emissions of successor equipment developed in the future compared to the current models, and is continually making efforts to reduce our emissions.
Selecting products with a low power consumption and high efficiency has always been one of our customers’ selection criteria, and the DISCO group recognizes that these are aspects that can be used to promote the sales of our products. However, going forward, as the transition to a decarbonized society picks up speed, we believe that these aspects will be even more important. Thus, in order to contribute to our customers’ energy-saving efforts even further, the DISCO group is committed to achieving top-class environmental performance in our products in the industry.
Risk Management
DISCO’s environmental departments at the head office and all manufacturing sites collaborate and identify the risks (transitional risks and physical risks) that could impact business activities in the mid-to-long term. In order to respond to the identified risks, the Company-wide Environmental Committee assesses the impact, proposes countermeasures, and monitors the situation. In addition, a system where the risks that are deliberated at the Company-wide Environmental Committee are reported at the Executive Committee and the Board of Directors meeting as and when necessary is in place in order to strengthen the risk countermeasures management system.
For physical risks, the BCM Committee devises countermeasures and monitors the implementation status as and when needed. DISCO established the BCM (Business Continuity Management) system in 2003, and has established a BCM Committee comprised of executives, with the President as the chairperson. The BCM Committee is held every month after the Board of Directors meeting, and Outside Directors participate in the committee as observers.
Metrics and Targets
The DISCO group considers taking countermeasures against climate change its social responsibility, and we have reduced emissions of greenhouse gases associated with our business activities. In 2021, the following mid- and long-term objectives were set as new targets for the reduction of greenhouse gases.
Mid-term objective:
“To achieve carbon neutrality for all emissions produced as a result of business activities (Scope 1 and 2) by 2030”
Long-term objective:
“To achieve carbon neutrality for all emissions produced as a result of the entire supply chain (Scope 1, 2, and 3) by 2050”
The DISCO group also views the CO2 emitted in the use of our products as very important, and we promote various activities with the aim of designing products that reduce CO2 emissions.
Environmental Activities and Data
In order to realize a sustainable society, the DISCO group strives to reduce toward greenhouse gas emissions, conserve resources, and reduce waste.
More environmental data and details regarding the DISCO group’s efforts can be found here.


